No products
Beauty & Lifestyle
Refine
Extra
Viewed Products
-

Off-White - Cobalt Blue Slick Long Dress - Exclusive Luxury Collection
Off White Dress Woman Slick Long Dress.
Beauty & Lifestyle
-
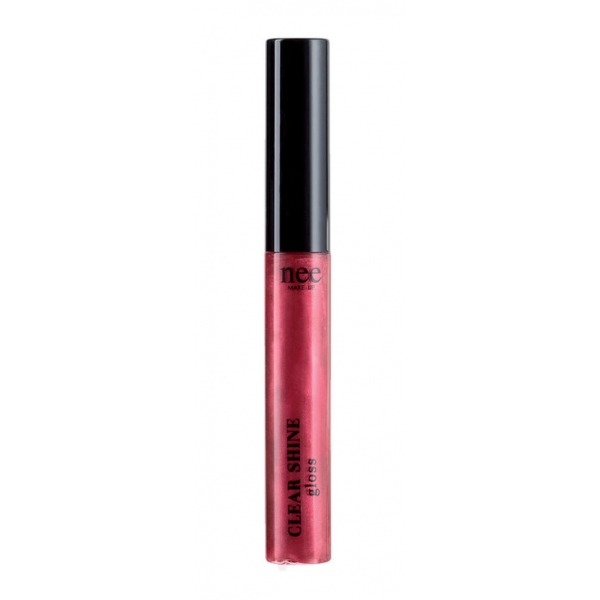
Nee Make Up - Milano - Clear Shine Gloss - Shy Cherry - Lips - Professional...
A real secret of youth for the lips! The innovative natural stabilized peptide stimulates the natural production of collagen and hyaluronic acid, for smooth and well-defined lips. The particular blend of jojoba oil and almond with shea butter makes the lips moisturized and rejuvenated, enhancing cell renewal and making the lips more elastic. Hyaluronic...
22,50 € -
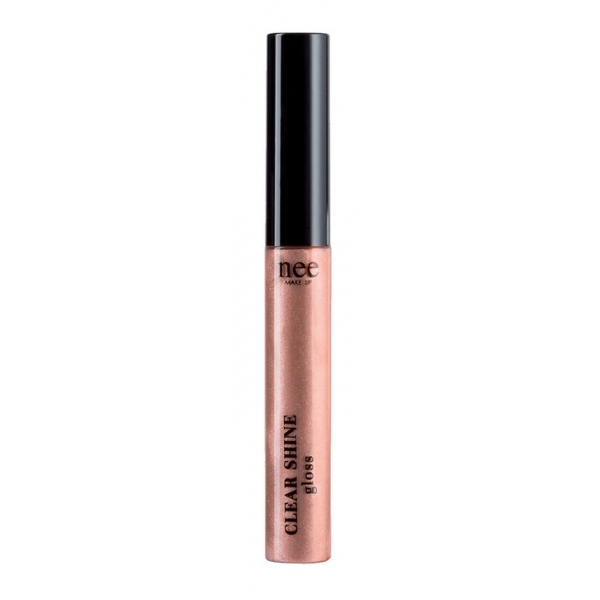
Nee Make Up - Milano - Clear Shine Gloss - All The Stars - Lips -...
A real secret of youth for the lips! The innovative natural stabilized peptide stimulates the natural production of collagen and hyaluronic acid, for smooth and well-defined lips. The particular blend of jojoba oil and almond with shea butter makes the lips moisturized and rejuvenated, enhancing cell renewal and making the lips more elastic. Hyaluronic...
22,50 € -
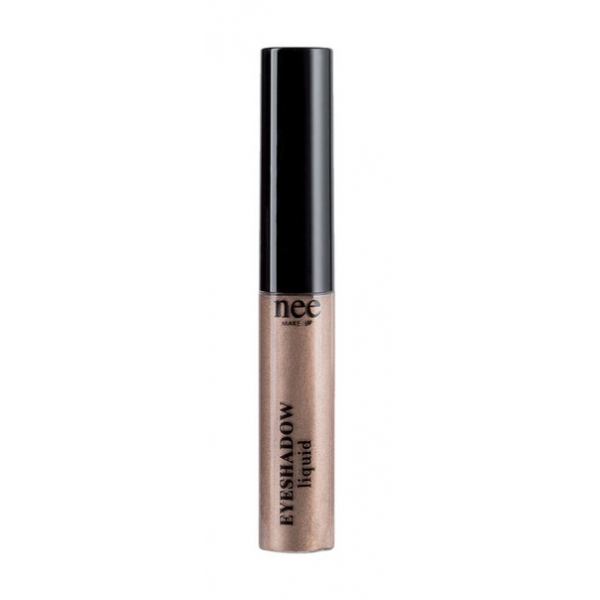
Nee Make Up - Milano - Eyeshadow Liquid Carribean - Eyes - Professional Make Up
A cascade of pearls for a bright and long lasting look. A liquid eyeshadow with a metallic finish for a shimmering and magnetic look. Velvety texture, easy to spread and blend thanks to the comfortable applicator, for an intense and bold result. The pearl particles are fixed to the eyelid for an amplified glow effect. Brilliant finish with extreme hold.
23,10 € -
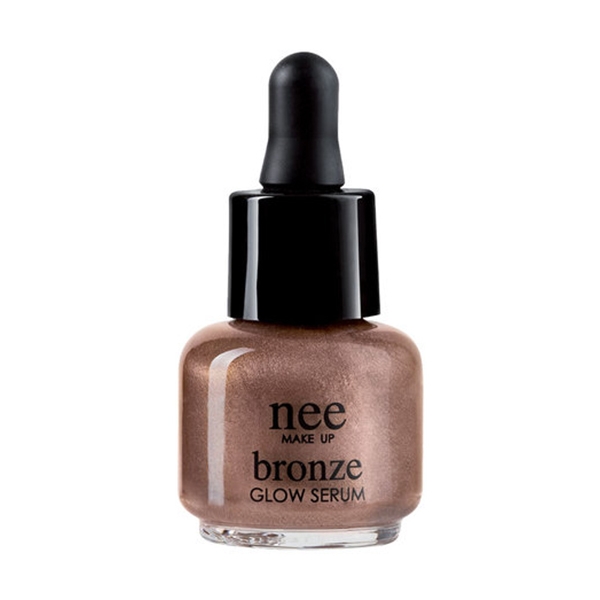
Nee Make Up - Milano - Bronze Glow Serum - Face - Professional Make Up
Nee Make Up Milano introduces a new bronze shade for the multitasking serum with illuminating pearls and vitamin E, a radiant and metallic finish for a slight all-over glow. Its non-greasy, extremely light texture is designed for every type of skin, non-greasy and does not clog pores. Bronze Glow Serum can be worn alone, as an illuminant to create light...
28,70 € -
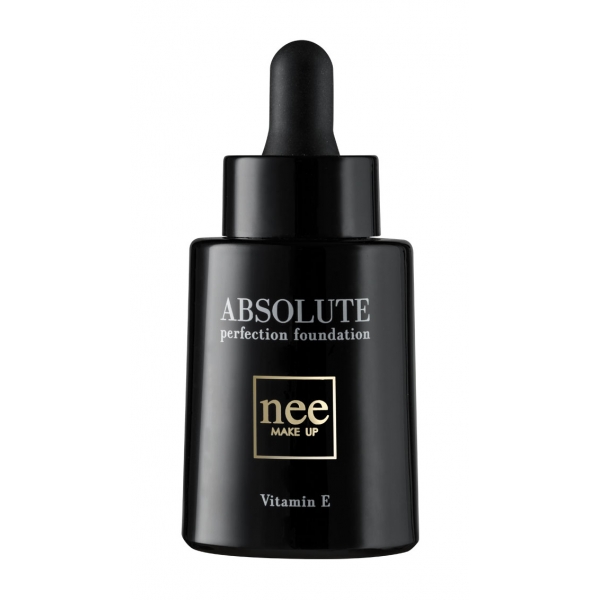
Nee Make Up - Milano - Absolute Perfection Foundation Warm Beige - New Glam...
New shade for the iconic foundation Nee Make Up Milan. An ideal color for the new season, it warms and brightens the complexion. Spectacular result, maximum hydration, an even wider range of nuances to choose your favorite color.
45,50 € -
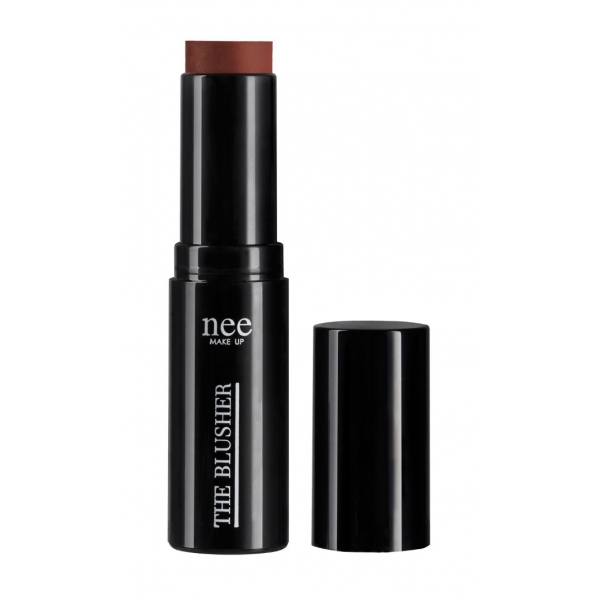
Nee Make Up - Milano - The Blusher Chocolate Glow - Blush - New Glam...
A touch of color on the cheeks will immediately make you feel glamorous! New texture for the fall-winter version of The Blusher. Trendy nuance, extraordinary glow effect, sculpts the features and makes the face shine with elegance. Incredibly creamy texture, easy to blend, second skin effect.
30,30 € -
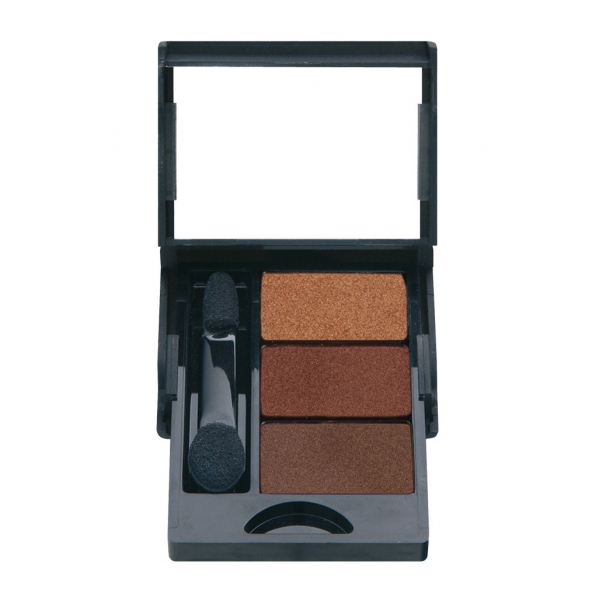
Nee Make Up - Milano - Eyeshadow Trio Sophi - Palettes - New Glam Collection...
Get different and fabulous looks in seconds thanks to the new trio mini eye shadow palette. Each nuance is rich in pigments and its velvety texture remains flawless and in place all day. Bright and glow shades blend perfectly with each other to adapt to any type of complexion and brighten the look. These eyashadow trio are the ideal choice if you want...
28,70 € -
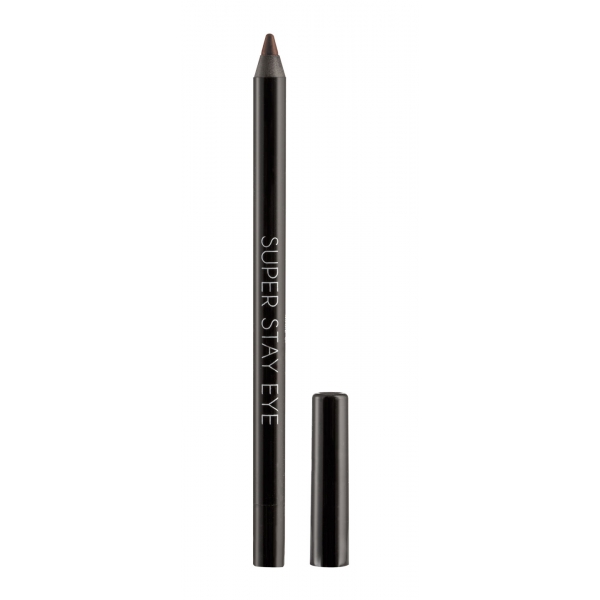
Nee Make Up - Milano - Super Stay Eye Kajal 24h Ebony - New Glam Collection -...
The pencil 24 h is characterized by its nuance, an intense brown that enhances the eye to the maximum. Its highly pigmented formula, its creamy and smooth mine give precise and perfect lines. Easily blendable both along the upper eyelash line and in the inner rim of the eye. Waterproof effect. Resistance test guaranteed up to 24 hours.
20,70 € -
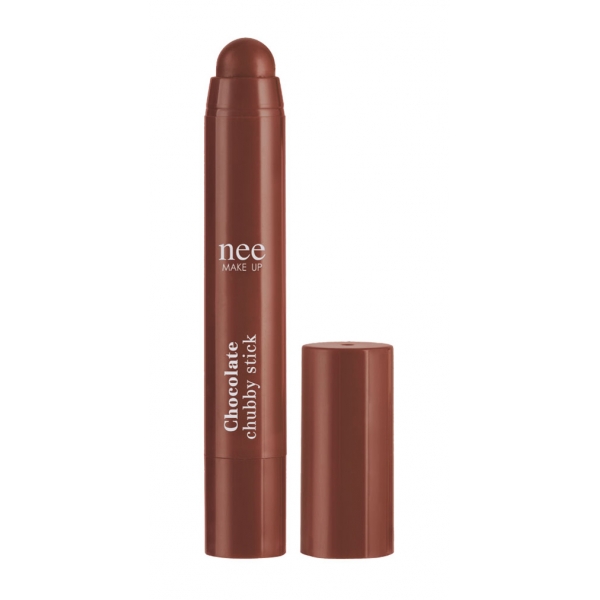
Nee Make Up - Milano - Chubby Stick Chocolate - New Glam Collection - Lips -...
Lipstick with an ultra sensory texture, a cuddle of beauty and hydration for the lips. The color melts instantly, illuminating the smile. The mix of light and precious oils present in the formula gives a brilliant finish and long-lasting comfort, accompanied by a delicate scent of delicious and enveloping chocolate.
25,40 € -
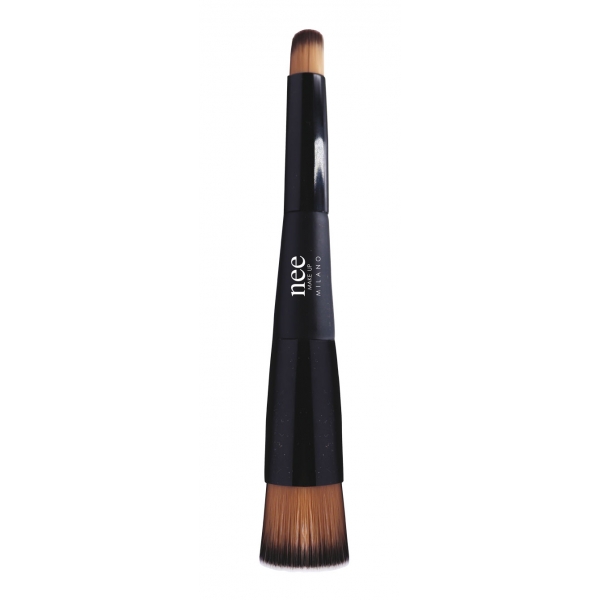
Nee Make Up - Milano - Two-in-One Brush Foundation & Concealer - New Glam...
Multi-function brush. Double applicator for foundation and concealer. On the one hand, the foundation brush allows both liquid and compact formulas to be spread evenly. On the other side, the smaller brush allows the concealer to be applied precisely even on the smallest areas or in the periocular area.
44,90 € -
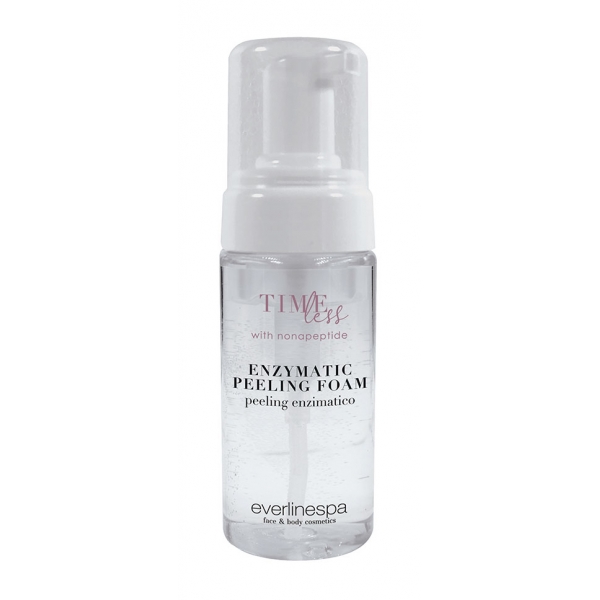
Everline Spa - Perfect Skin - Enzymatic Peeling Foam - Timeless - Anti Age...
Micro-exfoliating foam lotion enriched with glycolic acid. Renews the epidermal surface, eliminating dead cells. Improves skin texture, reduces fine lines, gives more radiance to the complexion that is more compact and smooth. Use at most twice a week is recommended.
37,70 € -
Everline Spa - Perfect Skin - Face Cream - Timeless - Anti Age Treatment -...
New generation facial treatment, effectively acts on the nourishment and firmness of the skin, thanks to an exceptional formulation, a concentration of very high level active ingredients and a velvety sensoriality. Thanks to the innovative nonapeptide it promotes cell renewal. Smoothes, repairs and protects thanks to a biotechnological complex based on...
56,10 € -
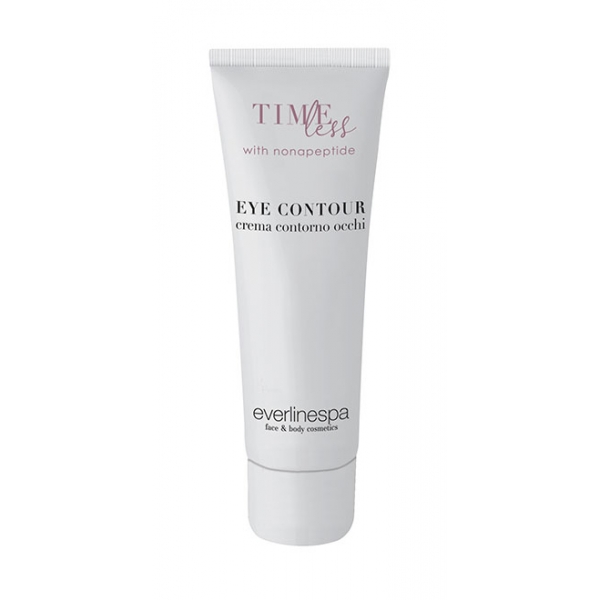
Everline Spa - Perfect Skin - Eye Contour Cream - Timeless - Anti Age...
Gives uniformity and compactness to the eye area. It acts on the microcirculation and on the bags, reduces dark circles and swelling thanks to the innovative nonapeptide. It nourishes and brightens, provides an anti-fatigue effect for a more youthful appearance and a more intense look.
52,40 € -
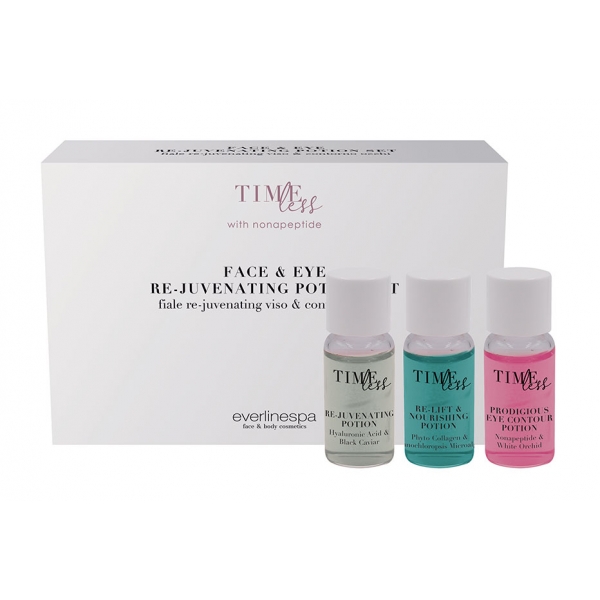
Everline Spa - Perfect Skin - Face & Eye Re-Juvenating Potion Set - Timeless...
An exclusive set of intensive youth. It contains three ampoules with a maximum concentration of active ingredients for intensive and personalized treatments.
56,80 € -
Everline Spa - Perfect Skin - Night Cream - Timeless - Anti Age Treatment -...
Essential night treatment for a beauty awakening. A rich cream, intensive nourishing, enriched with the innovative nonapeptide, vitamin E, rosehip oil and a complex based on microalgae Nannochloropis oculata, rich in vitamin C and B12. Upon awakening the skin is relaxed and luminous, full of vitality. The look appears radiant and full of charm.
56,10 € -
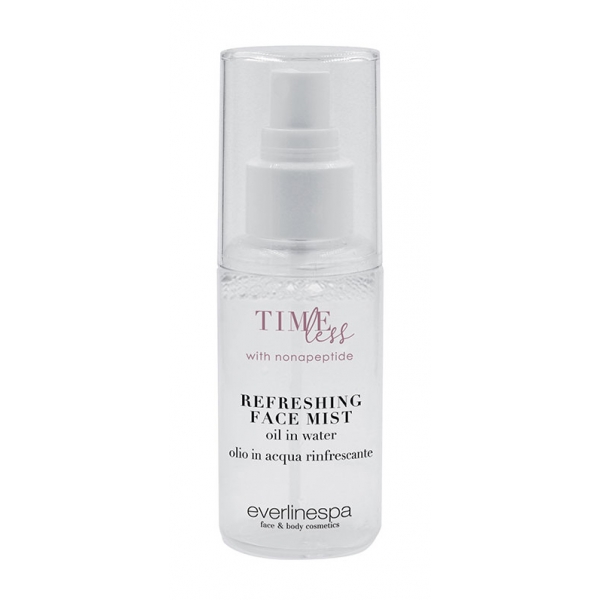
Everline Spa - Perfect Skin - Refreshing Face Mist Oil in Water - Timeless -...
A very light cloud of micro particles to deeply nourish the skin. It tones and prepares the skin for treatments, improving the results, as well as giving it a surplus of freshness during the day thanks to the imperceptible droplets of oil in water of centripole rose that gently quench the skin. The complexion is naturally brighter and healthier.
43,50 € -
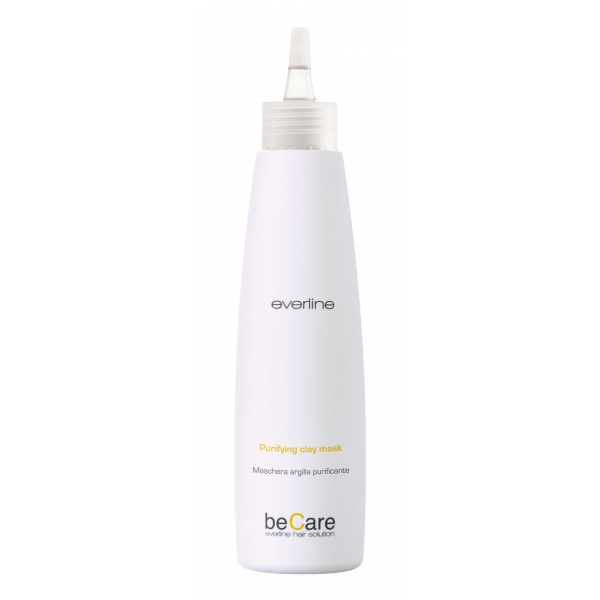
Everline Spa - Perfect Skin - Purifying Clay Mask - Perfect Skin - Body -...
Purifying hair mask for skin with excessive sebum production. The mix of clays, white and green, combined with essential oils keep the scalp clean and fresh.
29,00 € -
Advance - Essence - Home Fragrance - Exclusive Fragrance
Home fragrance 50 ml.
12,80 € 16,00 € -20%Reduced price ! -
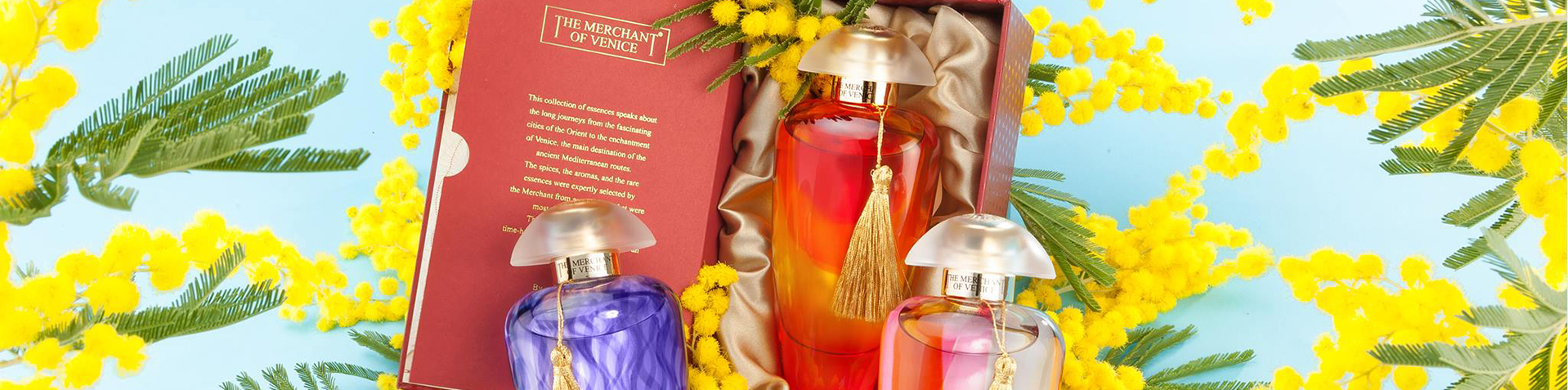
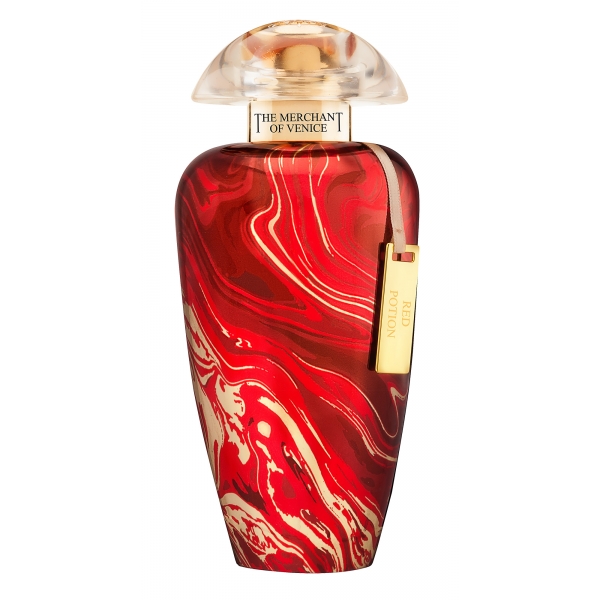
The Merchant of Venice - Red Potion - Murano Collection - Luxury Venetian...
As all the fragrances of Murano Collection, Red Potion resumes the elegance and nobility that characterized the society of the Serenissima. The richness of this original fragrance is underlined by the transparent cap that complete the mistery of the red bottle.
120,00 € -
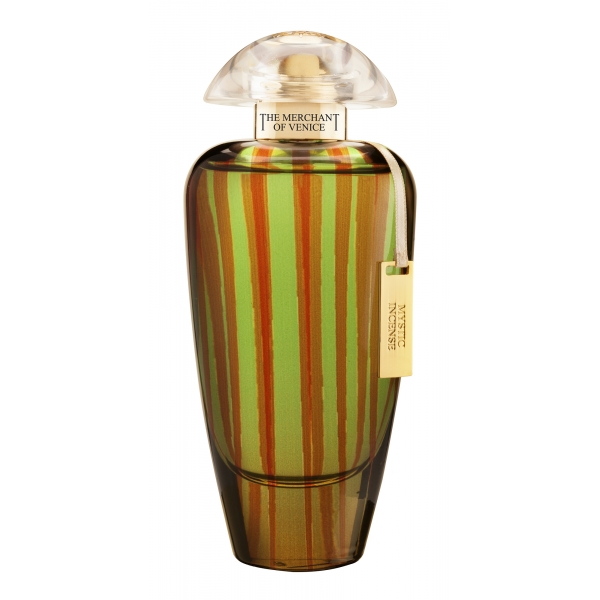
The Merchant of Venice - Mystic Incense - Murano Collection - Luxury Venetian...
Mystic Incense is a new and sophisticated interpretation of incense, an oily resin exuded by the Boswellia plants, typical of the Arabian Peninsula and Africa. Elegant and persuasive, it creates a perfect woody and gourmand accord. The base note confirms the vigorous personality of this fragrance through cocoa essence, while the incense is warmed by musky...
132,00 € -
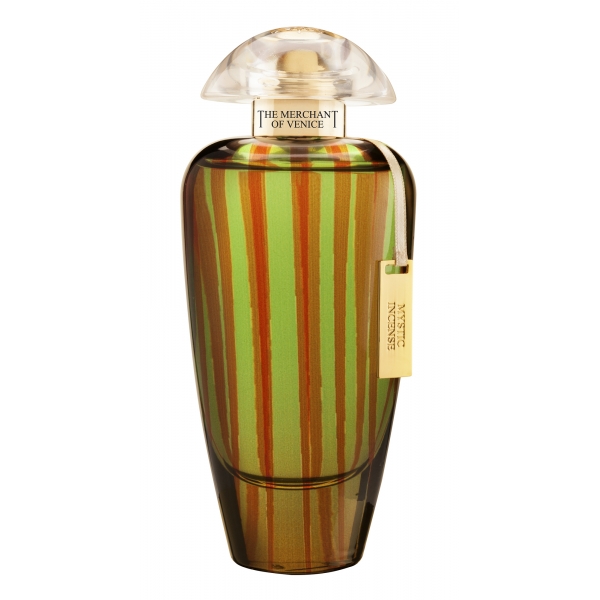
The Merchant of Venice - Mystic Incense - Murano Collection - Luxury Venetian...
Mystic Incense is a new and sophisticated interpretation of incense, an oily resin exuded by the Boswellia plants, typical of the Arabian Peninsula and Africa. Elegant and persuasive, it creates a perfect woody and gourmand accord. The base note confirms the vigorous personality of this fragrance through cocoa essence, while the incense is warmed by musky...
90,00 €